software process is the dictated steps to build a software.
It brings control and order and prevents chaos.
Quality, dead lines and long-term viability indicate success of the project.
a generic process model
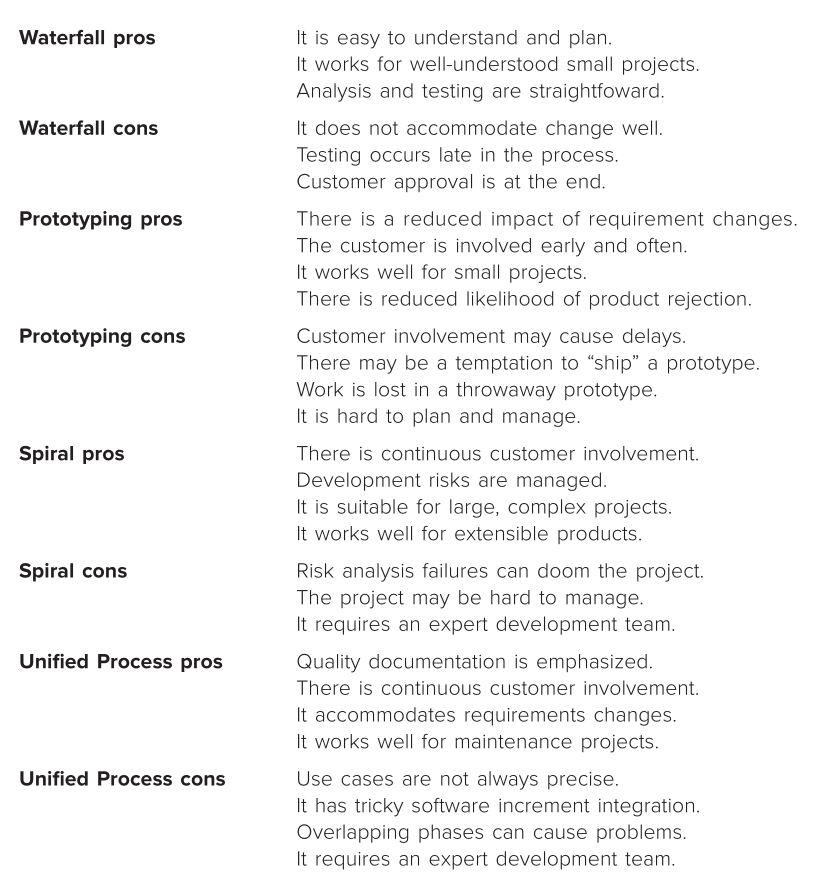
 linear process flow: executes each of the 5 framework activities in sequence.
linear process flow: executes each of the 5 framework activities in sequence.
Interactive PF: repeats one or more activities a few times before proceeding to next activity.
Evolutionary PF: executes activities in a circular way and after each circuit software is more complete.
Parallel PF: two or more activities happen at the same time.
defining a framework
a framework need to be adjusted considering by size of the project
identifying a task set
Defines the actual work that needs to be done.
A task set should be adapted to best suit the project and project team.
process assessment and improvement
projects advance can be metered using metric methods.
prescriptive process models
sometimes called triditional process models
the waterfall model
it’s used when requirements are well understood and are stable.
Mostly used for making changes to current software.
AKA linear sequential model.
This model problems:
- real world projects rarely follow a sequential flow
- it’s difficult to estimate all needs at the beginning
- customer must wait a long time to see any result
- critical problems won’t be detected until late in the project
prototyping process model
prototyping will clarify final needs when requirements are vague.
Can be included as part of a process or be a process itself.
Used to identify software requirements.
Problems are:
- stakeholders might misunderstood a prototype as final product
- temporary parts might stay in software for ever
- prototypes can evolve into final product
evolutionary process model
spiral model
It’s combination of iterative and waterfall models.
In this model software is developed in a series of evolutionary releases.
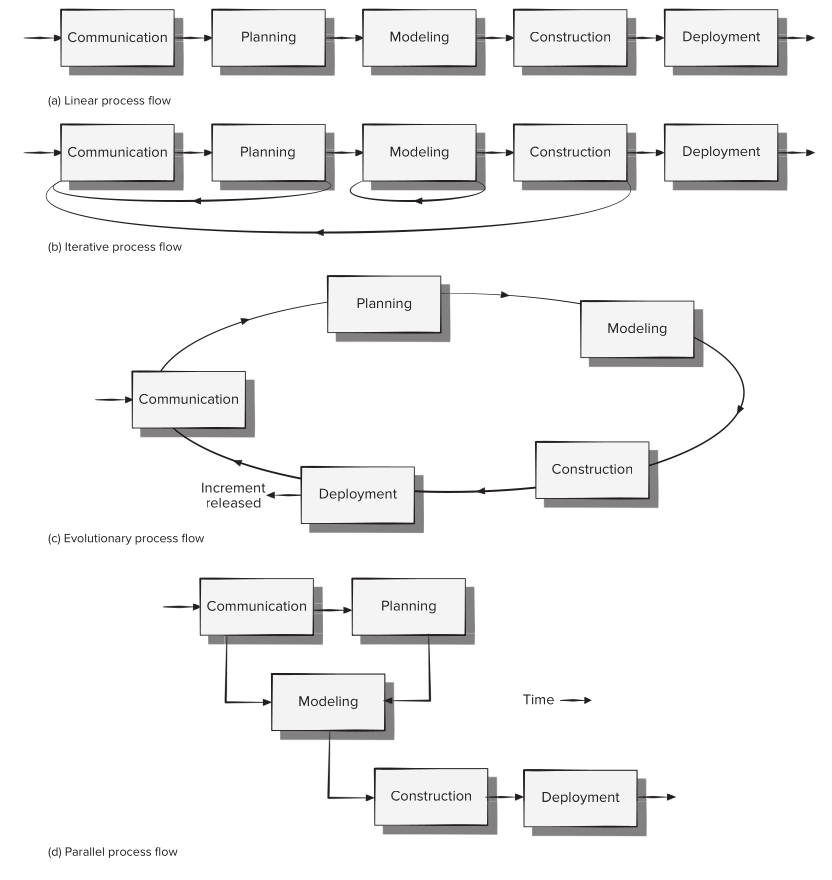
a typical spiral model:
First circuit around the spiral might result in making the project specification, and second one can end up making a prototype and then more sophisticated versions of software can be adapted throughout the software life.
It is suitable for big software projects.
Uses prototyping for risk reduction.
It emphasizes flexibility, extensibility and speed of development.
Making a balance between these process parameter and customer satisfaction is the challenge.
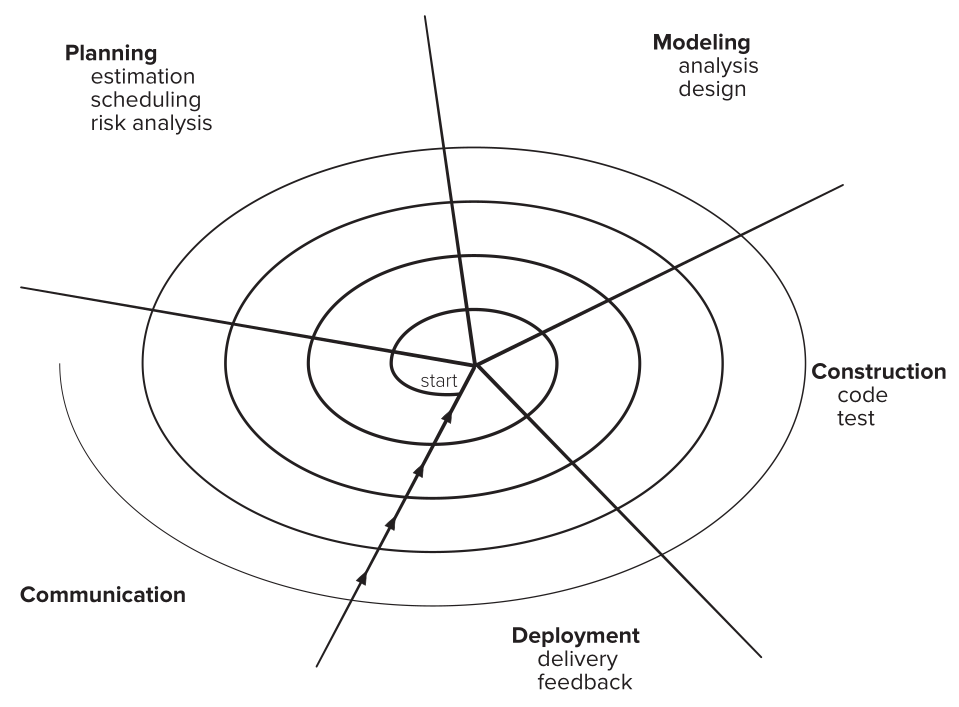
unified process model
It tries to draw on traditional software projects but characterize them to adapt agility.
UML is a language created for modeling. It best works for object oriented software development.
the unified process
- at inception phase communication and plannings happen and business needs and final features and functions are described.
- at elaboration phase preliminary use cases and 5 different views of software (use case, analysis, design, implementation, deployment) are refined.
- at construction phase code and tests are generated and features are tested before release.
- at transition phase documents and beta software are delivered and at the end of this stage a usable software is available.
- at production phase reports are monitored and request for fixes and changes are submitted.
Phases might not happen on a sequence
product and process
Comparing process models: